Using Science Process Skills, Reading to Learn and Writing to Communicate
Using Science Process Skills, Reading to Learn and Writing to Communicate: Overview
In this topic, we will go through various examples that enhance our learning skills. We will learn how we should proceed to do an experiment or to divide things into categories. It also explains some terms related to processing skills.
Important Questions on Using Science Process Skills, Reading to Learn and Writing to Communicate
Using a Celsius thermometer, Ram finds that water boils at _____ oC.
The units for measuring temperature on a thermometer are
What are some of the ways to display data?
Why is mathematics called the "Queen of Science'?
It is fine to use handspan while measuring the length of leaves while doing a scientific study of their sizes.
A boy is trying to find the density of different types of objects such as a block of wood, a steel spoon, a glass paperweight, a piece of stone. What is one of the measuring devices used here?
Which should be done first, displaying the data or recording the data? (Write in single word, either Display or Record.)
We may write a letter in:
Whether a graph is used to display the data or measure the data? (Write in single word, either display or measure.)
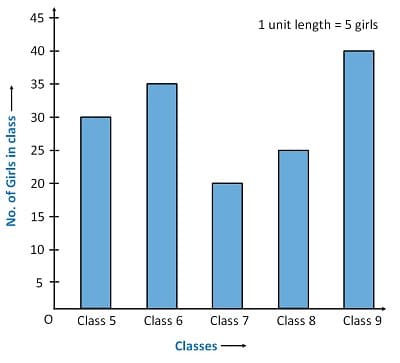
Which of the following cannot be concluded from the given graph?
_____ (Predict/Hypothesis) is the process skill that form an idea of an expected outcome based on observation or experience.
Which of the following is not a science process skill?
Spring balance is used to measure:
Scientists use number when:
In expressive writing, we may describe something, give example, or tell a story.
In _____ writing, we may write letters about important issues in science.
Displaying of data refers to:
Choose the correct sequence.
_____ (Measure/Record) refers to comparing the attributes of an object such as mass, length, etc.
Classify refers to grouping or organising objects or events in categorises based on species characteristics.
